【背景】
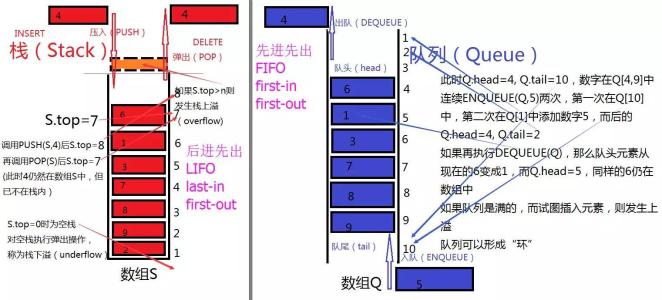
栈(stack)又名堆栈,它是一种运算受限的线性表。其限制是仅允许在表的一端进行插入和删除运算。这一端被称为栈顶,相对地,把另一端称为栈底。向一个栈插入新元素又称作进栈、入栈或压栈,它是把新元素放到栈顶元素的上面,使之成为新的栈顶元素;从一个栈删除元素又称作出栈或退栈,它是把栈顶元素删除掉,使其相邻的元素成为新的栈顶元素。
队列是一种特殊的线性表,特殊之处在于它只允许在表的前端(front)进行删除操作,而在表的后端(rear)进行插入操作,和栈一样,队列是一种操作受限制的线性表。进行插入操作的端称为队尾,进行删除操作的端称为队头。
【源码运行环境】
操作系统:MAC OS X 10.13.4
编译环境:CLion (C++ 14) cmake
【源码实现】
S_Q.h源码部分:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 | //// Created by WellLee on 2018/10/29.//#ifndef STACK_Queue_S_Q_H#define STACK_Queue_S_Q_H#include "stdio.h"#include "stdlib.h"#include "memory.h"/* * 说明:define 定义一些常用的符号特性 * 作用:增加代码可读性 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified: 2018年10月31日23:16:07 */#define TRUE 1#define FALSE 0#define OVERFLOW -1#define MAXSIZE 20typedef int Status;typedef int Elem;/* * 结构:顺序栈 * 作用:定义了顺序栈的一些结构特性,封装了常用的线性表操作 * Author: WellLee * Last modified: 2018年10月31日23:17:31 */typedef struct Stack{ Elem data[MAXSIZE]; int top;}Stack;Status InitStack(Stack *S);Status pop(Stack *S, Elem *e);Status push(Stack *S, Elem e);Status EmptyStack(Stack S);Status ClearStack(Stack *S);Status StackLength(Stack *S, int *length);Status DestroyStack(Stack *S);void showStackElements(Stack S);/* * 结构:链栈 * 作用:定义了链栈的一些结构特性,封装了常用的线性表操作 * Author: WellLee * Last modified: 2018年10月31日23:17:31 */typedef struct Stacknode{ Elem elem; struct Stacknode *next;}stacknode,*StackNode;typedef struct LinkStack{ StackNode top; int length;}*LStack;Status InitLinkStack(LStack *LS);Status LS_push(LStack *LS, Elem e);Status LS_pop(LStack *LS, Elem *e);Status LS_Clear(LStack *LS);Status LS_Destroy(LStack *LS);Status LS_Empty(LStack LS);void LS_show(LStack LS);/* * 结构:顺序队列 * 作用:定义了顺序队列的一些结构特性,封装了常用的线性表操作 * Author: WellLee * Last modified: 2018年10月31日23:17:31 */typedef struct SequenceQueue{ Elem data[MAXSIZE]; int front; int rear;}SqQueue;Status InitSqQueue(SqQueue *Q);Status EnSqQueue(SqQueue *Q, Elem e);Status DeSqQueue(SqQueue *Q, Elem *e);Status ClearSqQueue(SqQueue *Q);Status DestroySqQueue(SqQueue *Q);Status QueueLength(SqQueue Q, int *length);void showQueueElements(SqQueue Q);/* * 结构:链队列 * 作用:定义了链队列的一些结构特性,封装了常用的线性表操作 * Author: WellLee * Last modified: 2018年10月31日23:17:31 */typedef struct QueueNode{ Elem data; struct QueueNode *next;}QNode,*QNodeptr;typedef struct LinkQueue{ QNodeptr rear; QNodeptr front;}LinkQueue;Status InitLkQueue(LinkQueue *Q);Status EnLkQueue(LinkQueue *Q, Elem e);Status DeLkQueue(LinkQueue *Q, Elem *e);Status ClearLkQueue(LinkQueue *Q);Status DestroyLkQueue(LinkQueue *Q);Status LkQueueLength(LinkQueue Q, int *length);void showLkQueue(LinkQueue Q);#endif //STACK_Queue_S_Q_H |
Stack.c源码部分:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 | //// Created by WellLee on 2018/10/29.//#include "S_Q.h"#include "time.h"/* * 方法名:InitStack * 作用:初始化顺序栈 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified:2018年10月31日23:21:09 */Status InitStack(Stack *S){ S->top = -1; int StackLength = 0; Elem elem; srand(time(0)); printf("请输入栈的元素个数"); scanf("%d", &StackLength); for (int i = 0; i < StackLength; i++) { elem = rand() % 100 - 1; push(&*S, elem); } return TRUE;}/* * 方法名:push * 作用:顺序栈压栈操作 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified:2018年10月31日23:21:09 */Status push(Stack *S, Elem e){ if(S->top >= MAXSIZE) { printf("栈满\n"); return OVERFLOW; } S->data[++S->top] = e; return TRUE;}/* * 方法名:StackEmpty * 作用:判断顺序栈是否为空 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified:2018年10月31日23:21:09 */Status StackEmpty(Stack S){ if(S.top == -1) { return TRUE; } return FALSE;}/* * 方法名:pop * 作用:顺序栈出栈操作 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified:2018年10月31日23:21:09 */Status pop(Stack *S, Elem *e){ if(StackEmpty(*S)) { printf("栈空\n"); return FALSE; } int top = S->top; *e = S->data[S->top--]; S->data[top] = 0; return TRUE;}/* * 方法名:showStackElements * 作用:显示顺序栈元素 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified:2018年10月31日23:21:09 */void showStackElements(Stack S){ if(StackEmpty(S)) { printf("栈空\n"); return; } printf("栈元素如下:"); printf("栈顶指向 -> %d \n",S.top); for(int i = 0; i <= S.top; i++){ printf("%d ",S.data[i]); } printf("\n");}/* * 方法名:DestroyStack * 作用:销毁顺序栈 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified:2018年10月31日23:21:09 */Status DestroyStack(Stack *S){ free(S); return TRUE;}/* * 方法名:ClearStack * 作用:清空顺序栈 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified:2018年10月31日23:21:09 */Status ClearStack(Stack *S){ memset(S->data,0, sizeof(S->data)); S->top = -1; return TRUE;}/* * 方法名:StackLength * 作用:获取顺序栈长度 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified:2018年10月31日23:21:09 */Status StackLength(Stack *S, int *length){ *length = S->top + 1; return TRUE;}/* * 方法名:InitLinkStack * 作用:初始化链栈 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified:2018年10月31日23:21:09 */Status InitLinkStack(LStack *LS){ srand(time(0)); StackNode head = (StackNode)malloc(sizeof(stacknode)); if(!head) { printf("内存不足\n"); return OVERFLOW; } head->next = NULL; *LS = (LStack)malloc(sizeof(LStack)); if(!*LS) { printf("内存不足\n"); return OVERFLOW; } LStack ls = *LS; ls->top= head; ls->length = 0; printf("请输入栈的元素个数:"); int length; scanf("%d", &length); for(int i = 0; i < length; i++) { Elem e = rand()%100 -1; LS_push(&ls, e); } printf("初始化成功\n"); return TRUE;}/* * 方法名:LS_push * 作用:链栈压栈操作 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified:2018年10月31日23:21:09 */Status LS_push(LStack *LS, Elem e){ LStack ls = *LS; if(!ls) { printf("线性表参数有误\n"); return OVERFLOW; } StackNode head = ls->top; StackNode elem = (StackNode)malloc(sizeof(stacknode)); if(!elem) { printf("内存不足\n"); return OVERFLOW; } elem->elem = e; elem->next = ls->top->next; head->next = elem; ls->length++; printf("%d 入栈\n", e); return TRUE;}/* * 方法名:LS_pop * 作用:链栈出栈操作 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified:2018年10月31日23:21:09 */Status LS_pop(LStack *LS, Elem *e){ if(LS_Empty(*LS)) { printf("空栈,无元素出栈\n"); return OVERFLOW; } LStack ls = *LS; StackNode node = ls->top; StackNode freenode = node->next; *e = freenode->elem; node->next = freenode->next; free(freenode); ls->length--; printf("%d 出栈\n", *e); return TRUE;}/* * 方法名:LS_Clear * 作用:清空链栈 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified:2018年10月31日23:21:09 */Status LS_Clear(LStack *LS){ LStack ls = *LS; if(!ls){ printf("栈参数有误\n"); return FALSE; } while(ls->length != 0) { Elem temp; LS_pop(&ls, &temp); } printf("栈已清空\n"); return TRUE;}/* * 方法名:LS_Destroy * 作用:销毁链栈 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified:2018年10月31日23:21:09 */Status LS_Destroy(LStack *LS){ free(*LS); printf("栈已销毁\n"); return TRUE;}/* * 方法名:LS_Empty * 作用:判断链栈是否为空 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified:2018年10月31日23:21:09 */Status LS_Empty(LStack LS){ if(LS->length == 0) { return TRUE; } return FALSE;}/* * 方法名:LS_show * 作用:显示链栈元素 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified:2018年10月31日23:21:09 */void LS_show(LStack LS){ if(LS_Empty(LS)) { printf("空栈\n"); return; } StackNode head = LS->top->next; printf("当前栈有%d个元素,如下所示:\n",LS->length); while(head!=NULL) { printf("%d ",head->elem); head = head->next; } printf("\n");} |
Queue.c 源码如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 | //// Created by WellLee on 2018/10/31.//#include "S_Q.h"/* * 方法名:InitSqQueue * 作用:初始化顺序队列 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified:2018年10月31日23:42:16 */Status InitSqQueue(SqQueue *Q){ Q->front = 0; Q->rear = 0; return TRUE;}/* * 方法名:EnSqQueue * 作用:顺序队列入队操作 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified:2018年10月31日23:42:16 */Status EnSqQueue(SqQueue *Q, Elem e){ if((Q->rear + 1) % MAXSIZE == Q->front) { printf("队列满\n"); return OVERFLOW; } Q->data[Q->rear] = e; Q->rear = (Q->rear+1) % MAXSIZE; return TRUE;}/* * 方法名:DeSqQueue * 作用:顺序队列出队操作 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified:2018年10月31日23:42:16 */Status DeSqQueue(SqQueue *Q, Elem *e){ if(Q->rear == Q->front) { printf("队空\n"); return FALSE; } *e = Q->data[Q->front]; Q->front = (Q->front + 1) % MAXSIZE;}/* * 方法名:ClearSqQueue * 作用:清空顺序队列 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified:2018年10月31日23:42:16 */Status ClearSqQueue(SqQueue *Q){ memset(Q->data,0, sizeof(Q->data)); InitSqQueue(Q); return TRUE;}/* * 方法名:DestroySqQueue * 作用:销毁顺序队列 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified:2018年10月31日23:42:16 */Status DestroySqQueue(SqQueue *Q){ ClearSqQueue(Q); printf("队列已经销毁\n"); return TRUE;}/* * 方法名:QueueLength * 作用:获取顺序队列长度 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified:2018年10月31日23:42:16 */Status QueueLength(SqQueue Q, int *length){ *length = (Q.rear - Q.front + MAXSIZE) % MAXSIZE; return TRUE;}/* * 方法名:showQueueElements * 作用:输出顺序队列中的元素 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified:2018年10月31日23:42:16 */void showQueueElements(SqQueue Q){ int length = 0; QueueLength(Q, &length); if(length == 0) { printf("队空\n"); return; } printf("当前队列元素如下\n"); for(int i = 0; i < length; i++) { printf("%d ", Q.data[Q.front + i]); } printf("\n");}/* * 方法名:InitLkQueue * 作用:初始化链队 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified:2018年10月31日23:42:16 */Status InitLkQueue(LinkQueue *Q){ QNodeptr head = (QNodeptr )malloc(sizeof(QNode)); if(!head) { printf("内存不足\n"); return OVERFLOW; } head->next = NULL; Q->front = head; Q->rear = head; return TRUE;}/* * 方法名:EnLkQueue * 作用:链队压栈操作 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified:2018年10月31日23:42:16 */Status EnLkQueue(LinkQueue *Q, Elem e){ QNodeptr node = (QNodeptr )malloc(sizeof(QNode)); if(!node) { printf("内存不足\n"); return OVERFLOW; } node->data = e; node->next = NULL; Q->rear->next = node; Q->rear = node; return TRUE;}/* * 方法名:DeLkQueue * 作用:链队出栈操作 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified:2018年10月31日23:42:16 */Status DeLkQueue(LinkQueue *Q, Elem *e){ if(Q->rear == Q->front) { printf("队空\n"); return FALSE; } QNodeptr temp = Q->front->next; Q->front->next = temp->next; *e = temp->data; if(Q->front->next == NULL) { Q->rear = Q->front; } free(temp); return TRUE;}/* * 方法名:ClearLkQueue * 作用:清除链队所有数据 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified:2018年10月31日23:42:16 */Status ClearLkQueue(LinkQueue *Q){ while(Q->front != Q->rear) { Elem temp; DeLkQueue(Q, &temp); } return TRUE;}/* * 方法名:DestroyLkQueue * 作用:销毁链队 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified:2018年10月31日23:42:16 */Status DestroyLkQueue(LinkQueue *Q){ free(Q->front); return TRUE;}/* * 方法名:LkQueueLength * 作用:获取链队元素长度 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified:2018年10月31日23:42:16 */Status LkQueueLength(LinkQueue Q, int *length){ QNodeptr temp = Q.front->next; int i = 0; while(temp != NULL) { i++; temp = temp->next; } *length = i;}/* * 方法名:showLkQueue * 作用:显示链队所有元素 * Author: WellLee * Last Modified:2018年10月31日23:42:16 */void showLkQueue(LinkQueue Q){ QNodeptr temp = Q.front; temp = temp->next; if(temp == NULL) { printf("队空\n"); return; } printf("队列元素如下\n"); while(temp != NULL) { printf("%d ",temp->data); temp = temp->next; }} |
【分析】
-
栈和队列都是特殊的线性表,只不过是对插入和删除做了限制。
-
栈(Stack)是限定仅在表尾进行插入和删除操作的线性表。根据这样的特性又可以称它为:后进先出表(LIFO)。
-
队列(Queue)是只允许在一端进行插入操作,而在另一端进行删除操作的线性表。根据这样的特性又可以称它为:先进先出表(FIFO)。
-
它们均可以用线性表顺序存储结构来实现,但都存在顺序存储的一些弊端,因此它们各自有各自的技巧来解决这个问题。
-
对于栈来说,如果是两个相同数据类型的栈,可以用数组的两端作为栈底的方法来让两个栈共享数据,这就可以最大化利用数组的空间。
-
对于队列来说,为了避免数组插入和删除时需要移动数据,于是引进了循环队列,使得队头和队尾可以在数组中循环变化。解决了移动数据的时间损耗,使得原来的删除和插入式O(n)的时间复杂度编程了O(1)。
-
它们也都可以用链式存储来实现,实现原则上与线性表基本相同。
【总结】
本文通过学习栈和队列两种数据结构的定义,性质和实现方式,给出了栈/队列的C语言程序实现。加深了对栈/队列的认识,也接触了一些栈在计算机中的应用(递归,中缀->后缀表达式等)。也在从线性表表示栈/队列过程中学习到了一些前人解决问题的思想(共享栈、循环队列的引入)。而这两种数据结构的引入简化了程序设计的问题,划分了不同关注层次,使得思考范围缩小,更更加聚焦于我们要解决问题的核心。
【参考文献】
《大话数据结构》.程杰.清华大学出版社